MMIC Amplifiers Stretch the Boundaries of Dynamic Range in VHF/UHF Communications

The noise figure and linearity of low noise amplifiers are critical factors in maximizing sensitivity and dynamic range in RF receiver design. The amplifier noise figure determines the weakest signal the amplifier can discern, and the IP3 determines the degree to which intermodulation products from nearby signals interfere with the desired signal. The lower the noise figure and the higher the IP3 of the amplifier at the receiver input, the greater the sensitivity and Spurious Free Dynamic Range (SFDR) of the receiver.
בחירת מגברי MMIC בעלי ליניאריות גבוהה לשימוש בצורות גל ספרתיות מרוכבות

מגברי MMIC (מעגלים משולבים מונוליטיים לגלי מיקרו) המבוססים על טרנזיסטורי גאליום ארסנייד בטכנולוגית PHEMT במצב מורחב (enhanced mode) מספקים למשתמש יתרונות מבחינת ספרת הרעש בפס הרחב ומבחינת ביצועי האפנון ההדדי (intermodulation), אשר מבדילים אותם מהדורות הקודמים של תכנוני מגברי גאליום ארסנייד.
Selecting High Linearity MMIC Amplifiers for use with Complex Digital Waveforms

Enhanced Mode GaAs PHEMT (E-PHEMT) based MMIC amplifiers provide users advantages in both broadband noise figure and intermodulation performance, setting them apart from previous generations of GaAs amplifier designs. Historically known for their extremely low noise figure, PHEMTs have also been used extensively for power applications in the mobile PA market. Recent designs possess a combination of low noise and excellent suppression of intermodulation distortion, which improves both ends of the dynamic range over broad frequency range.
ביטול השימוש ב-Bias Tee במוצא של מגברי Push–Pull באמצעות שימוש בשנאי 3:1 לא מאוזן למאוזן TCM3–452X+
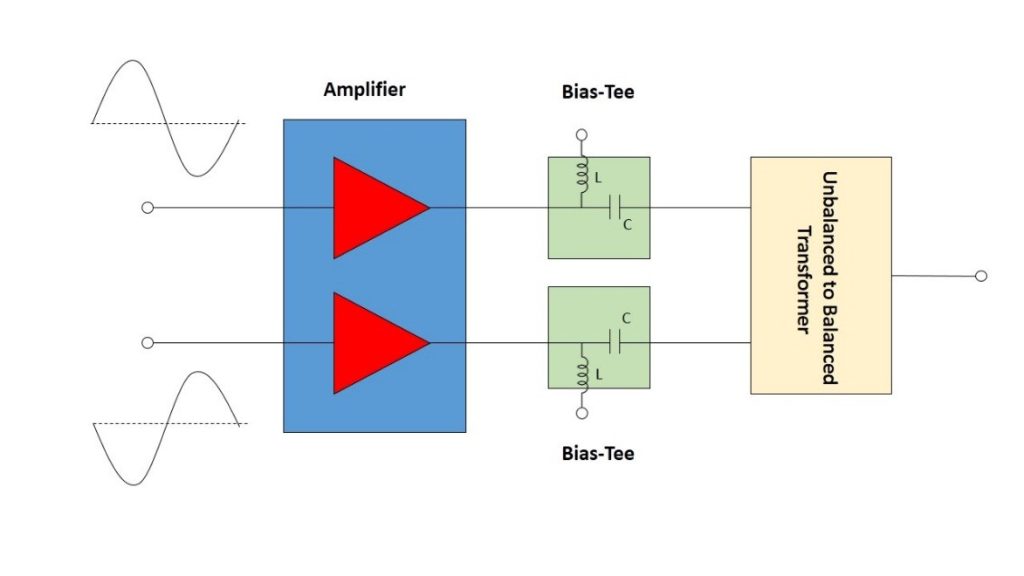
מגברי Push-Pull (דחף-סחב) משמשים במערכות מרובות אוקטבות כדי לשפר את הספק המוצא והנצילות של המגבר, לדכא הרמוניות לא רצויות ולשפר את הטווח הדינמי של המערכת. בתכנון של מגבר Push-Pull אות המקור מסופק לשני טרנזיסטורים או מגברים מתואמים במקביל וביחס מופע (פאזה) של 180º. כאשר מחברים אותם מחדש בעזרת התקן מסכם שני בהזזת מופע של 180º, האותות הבסיסיים נמצאים במופע אחד ובסיכום של פעמיים ההספק של כל מחצית, שעה שההרמוניות מסדר זוגי הן במופע הפוך, וכך מתבטלים באופן אידיאלי האותות הבלתי רצויים האלו. במציאות, חוסר האיזון של המופע והמשרעת (אמפליטודה) של מעגלי הפיצול והסיכום גורם ל”קלקול” של הביטול האידיאלי. עם זאת, התוצאה הנקייה היא עדיין דיכוי משמעותי של ההרמוניות הזוגיות, בדרך כלל ב- 20 dB עד 40 dB.
Eliminating Bias Tees from Push-Pull Amplifier Outputs Using TCM3-452X+ 3:1 Unbalanced-to-Balanced Transformer
Push-pull amplifiers are used in many multi-octave systems to enhance amplifier output power and efficiency, suppress unwanted harmonics and improve system dynamic range. In a push-pull amplifier design, two matched transistors or amplifiers are supplied by the source signal in parallel and at a 180° phase relationship. When re-combined through a second 180° phase shifting combiner, the fundamental signals are in-phase and combined at twice the power of each half, while the even order harmonics are out-of-phase, creating ideal cancellation of these unwanted signals. In reality, the phase and amplitude unbalance of the splitting-combining circuits result in degradation of the ideal cancellation. However, the net result is still significant suppression of the even harmonics, typically by 20 to 40 dB.




