Demystifying RF Transformers: A Primer on the Theory, Technologies and Applications – Part 1

In essence, a transformer is merely two or more conductive paths linked by a mutual magnetic field. When a varying magnetic flux is developed within the core by alternating current passing through one conductive path, a current is then induced in the other conductive paths. This induced current is proportional to the ratio of magnetic coupling between the two conductive paths. The ratio of the magnetic coupling of the conductive paths with the core determines the induced voltage in the additional conductive paths, providing both an impedance transformation and a voltage step-up or step-down. Additional conductive paths, potentially all with different coupling ratios, may be added to realize various functions, which is why RF transformers are such varied and versatile devices used widely throughout the RF/microwave industry.
מסנני מהוד קרמיים בעלי גורם איכות (Q) גבוה ליישומי GNSS
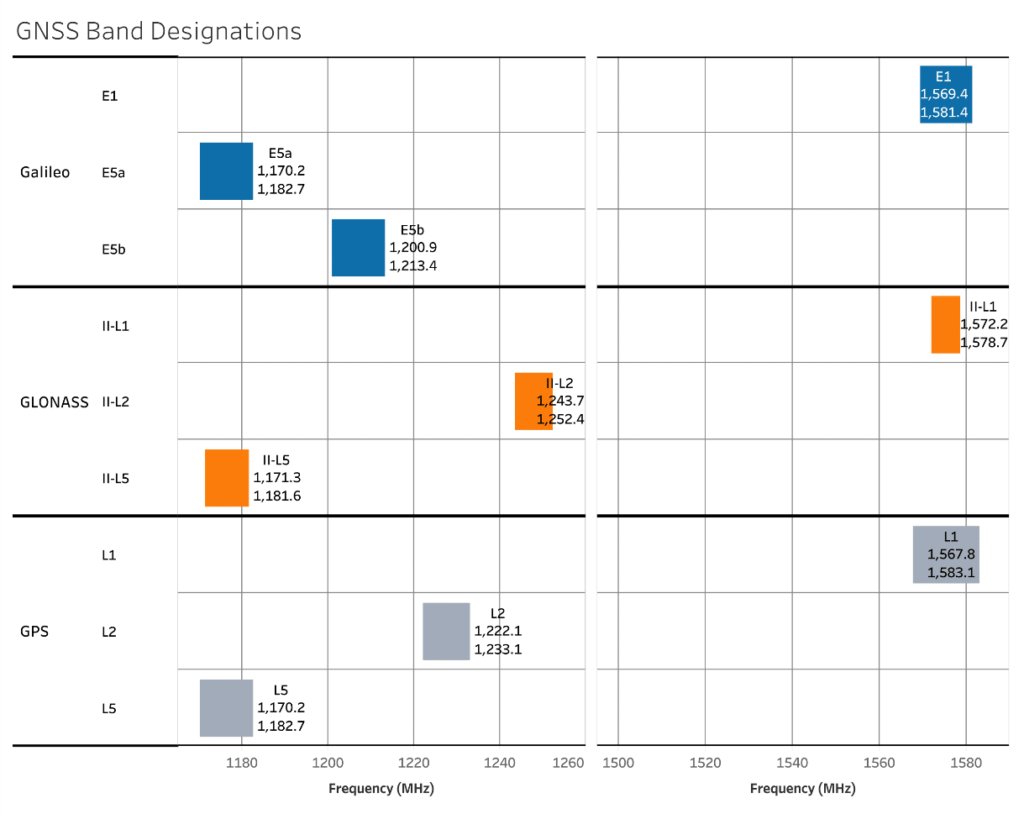
מערכות GNSS (מערכות ניווט גלובלי בעזרת לוויינים) הופכות יותר ויותר להיות יישום ת”ר ((RF נפוץ הן בשימושים צבאיים וגם בשימושים אזרחיים. טכנולוגיית GNSS מוקדמת או שירותים מבוססי מיקום (LBS), פותחה באופן בלעדי לשימושים צבאיים והופעלה עם שולי שגיאה של כ-9 מ’ (10 יארד), שהיו מספקים בזמנו, אבל הם הגבילו את התאמתה לשימושי קצה שלהם נדרשה דרגה גבוהה יותר של דיוק. בזמן שחלף מאז הושקו לראשונה השירותים של מערכת GPS, לפני יותר מ- 40 שנה, התפתחות הטכנולוגיה שיפרה את הדיוק עד כדי סדר של 1.83 – 2.74 מ’. התקדמות זו של הטכנולוגיה, בשילוב עם מזעור משמעותי והפחתת עלותם של התקנים מאופשרי שירותי LBS, פתחו שוק נרחב ומתפתח של שירותי GNSS. לדוגמה, מערכת GNSS משמשת כיום בתחום החקלאות לחישובים סטטיסטיים בנוגע למזג אוויר, לתנאי קרקע ולבריאות היבול, על מנת לעזור לחקלאים להגדיל למקסימום את היבולים ואת הרווחים שלהם. חידושים כאלה עודדו את הדרישה לרכיבים שתומכים ביישומים צבאיים ותעשייתיים וביישומי צריכה.
High-Q Ceramic Resonator Filters for GNSS Applications

GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite Systems) has become an increasingly prevalent RF application for both military and consumer use. Early GNSS technology, or location-based services (LBS), was developed exclusively for military use and operated with a margin of error of about 10-yards (9.14m), which was sufficient at the time, but limited its suitability for end uses requiring a higher degree of precision. In the time since the first launch of GPS more than 40 years ago, the evolution of the technology has improved precision to the order of 2-3 yards (1.83-2.74m). This advancement of the technology combined with significant miniaturization and cost reduction of LBS-enabled devices has opened up a large and growing commercial market for GNSS services. For example, GNSS is now used in the agricultural market to calculate statistics for weather, soil conditions, and crop health to help farmers maximize their yields and profits. Such innovations have stimulated demand for components that support military, industrial and consumer applications.
Understanding Lumped Element Filters
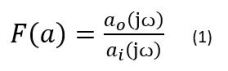
Before discussing filter designs and differentiating any given filter topology from another, it’s important to review the fundamentals of filter structures and their function. A filter is a two-port, passive, reciprocal device that allows frequencies within a given band to pass through while blocking signals outside the desired band.
There are many filter types available to the system design engineer including RLC filters, active RC filters, crystal filters, cavity filters, ceramic resonator filters and SIW, SAW and BAW filters. Filters may be fabricated using lumped elements, thin and thick film microstrip and stripline, LTCC and other manufacturing technologies. This article will focus on lumped element filters.
Impedance Matching Devices
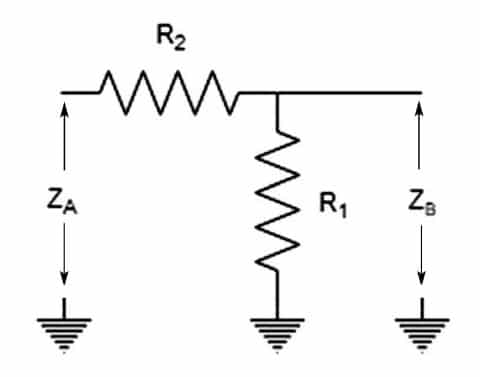
The impedance of a component or transmission line is a major concern when designing RF/microwave systems. At the circuit level, optimum performance is obtained when devices are matched to the desired system impedance, typically 50Ω or 75Ω. At the system level, each building block must be matched to the system impedance to maintain performance along the signal path.
Reflectionless Filter Basics: A Brief History of the Genesis of Reflectionless Filters
The advent of broad bandwidth amplifiers, analog-to-digital converters (ADCs), digital-to-analog converters (DACs), and software-defined radios has brought about growing interest in broadband communications, radar, and sensing applications. For these applications, there is often a need to preserve the highest sensitivity and dynamic range possible within the receiver signal chain and to mitigate the number and strength of harmonics and spurious content in the transmitter signal chain. This is a substantial challenge considering the nature of non-linear components within these circuits, namely compression-mode amplifiers, mixers, multipliers, and frequency-conversion electronics.
משיגים הצלחה כבר בסיבוב הראשון ברכיבי LTCC בעזרת מודלים מתקדמים של הדמיית חומרים
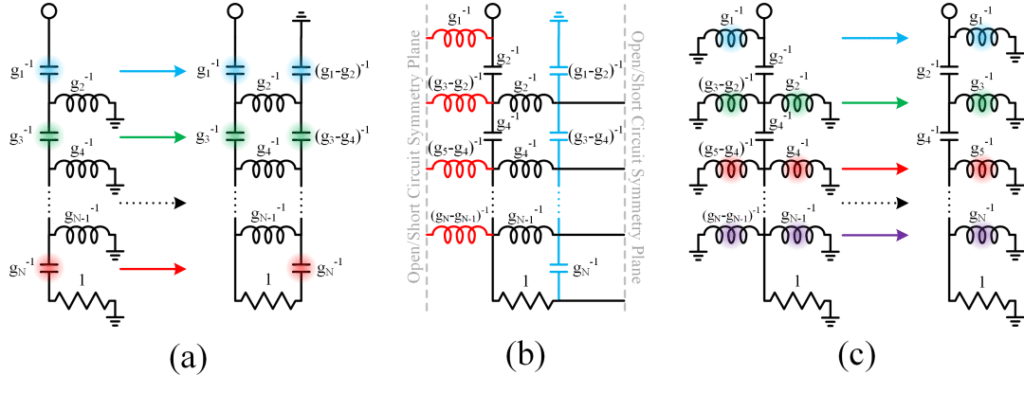
מאז הופעתה של ‘תיאוריית סינתזת רשתות’ (Network Synthesis Theory) בתחילת המאה ה- 21, מתכנני מסננים פיתחו פתרונות בעלי תחכום הולך וגובר, כדי לתרגם פונקציות מעבר פולינומיאליות לרכיבים פיסיים עובדים. גוף הידע על רכיבים מקובצים הוא מבוסס היטב על ‘התנך האדום הגדול’ של מסננים Microwave Filters, Impedance Matching Networks, and Coupling Structures, מאת מטאל, יאנג וג’ונס (Matthaei, Young and Jones), ועבור מבני צימוד בספר Microwave Filters for RF/Microwave Applications. הידע הזה, כשהוא משולב בזמינותם של כלי תוכנה מתקדמים לניתוח מסננים עם אלגוריתמים ממוסחרים לפתרון מקיף וממוחשב, כדוגמת שיטת המומנטים (MoM) ושיטת האלמנטים הסופיים (FEM), סיפקו למתכננים ערכת כלים רבת יכולת שמאפשרת לממש הן טופולוגיות ידועות וגם טופולוגיות שרירותיות.
Renewing Our Founding Values as a 50-Year-Old Startup

The Mini-Circuits story is well known to many in the RF and Microwave industry. Some know us for our advertising, some know us as one of the first companies to transform the pricing structure of RF components, and some know us through the personal relationships they had with Harvey Kaylie, our founder and chief executive for the first 50 years of our history.
FILTERING WITHOUT REFLECTIONS: Flattening Multiplier Chain Conversion Efficiency & More
A new class of filter, which exhibits broadband matched impedance at its ports, has recently been invented and made available. This new device, the reflectionless filter, has demonstrated a variety of benefits when used to replace conventional filters in a signal chain. This white paper briefly introduces the reflectionless filter and compares conventional filter and reflectionless filter behavior. Use cases are presented examining how reflectionless filters can improve system performance when used with mixers, ADCs, and receiver signal chains. Lastly, an experiment is described and test results presented to compare the conversion loss ripple in multiplier chains when reflectionless and reflective filters are used to filter spurious signals.
MINI-CIRCUITS ראיון עם מייסד ומנכ”ל הארווי קיילי

ש. : יישומים צבאיים היו מאז ומעולם מגזר קריטי בשוק העולמי של מוצרי ת”ר (RF) ומוצרי גלי מיקרו. איך אתה רואה את התפתחות השוק הצבאי בשנת 2018 ואילך, בהשוואה לשנים האחרונות?




