מסננים ללא החזרות משפרים לינאריות ותחום דינמי במערכות מיקרוגל
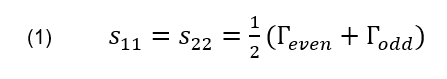
מסננים הם אבני יסוד בסיסיות כמעט בכל מערכת מודרנית של ת”ר (RF) או גלי מיקרו, שמשמשים לסילוק אותות בלתי רצויים בארכיטקטורות של מקלטים ומשדרים. עד לאחרונה, מחקרים שבוצעו בנושא התכנון המעשי של מסננים הוקדשו בעיקר לטופולוגיות שבהן הדחייה של תדירויות בפס החסימה הושגה על ידי החזרה של אותות לא רצויים אל המקור. באותו זמן, קיימים יישומים רבים שבהם החזרות אלו יוצרות תוצרים של אפנון ביניים, אדוות בהגבר (gain ripple) ובעיות נוספות בביצועי המערכת. למשל, התקנים לא ליניאריים כגון ערבלים, מכפלים ומגברים בעלי הגבר גבוה, שלהם יש תגובה בתדירויות מחוץ לפס, רגישים ביותר להחזרות שנגרמות על ידי תכנונים שגרתיים של מסננים. מצב זה הופך להיות מאתגר במיוחד, מפני שלא פעם המסננים נדרשים בסמוך או בצמוד להתקנים אקטיביים הנמצאים במסלול של האות, על מנת להגדיר טוב יותר את רוחב הפס או לדכא הרמוניות בלתי רצויות.
Impact of Date Code Age Restrictions on Quality, Service, and Value
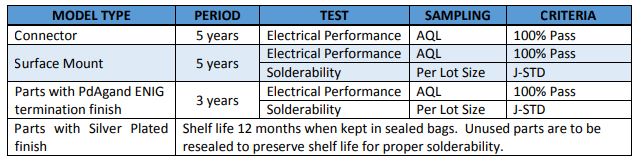
Extensive studies done by industry leaders, NASA and the U.S. military have shown substantial evidence that in modern storage environments, time intervals of five years or longer between manufacture of components and shipment to OEMs pose virtually no risk to the quality or reliability of electronic products. Date code based age restrictions were originally imposed due to concerns about age-related oxidation of eutectic (or tin-lead plated) parts and loss of component solderability. The subsequent replacement of tinlead solder with lead-free solder in RoHS compliant parts has since minimized the cause of this failure mechanism. Additionally, advances in product packaging and storage such as bagging, taping, and moisture control techniques now provide robust protection from electronic degradation and “out-of-the-box” failure due to age for time periods in the order of decades (i). As a result of such findings, the US military has eliminated date code requirements for electronic products altogether (ii), and NASA has significantly relaxed its standards, allowing a five year window before parts in storage are reviewed to determine the need for re-screening (iii).
ביטול השימוש ב-Bias Tee במוצא של מגברי Push–Pull באמצעות שימוש בשנאי 3:1 לא מאוזן למאוזן TCM3–452X+
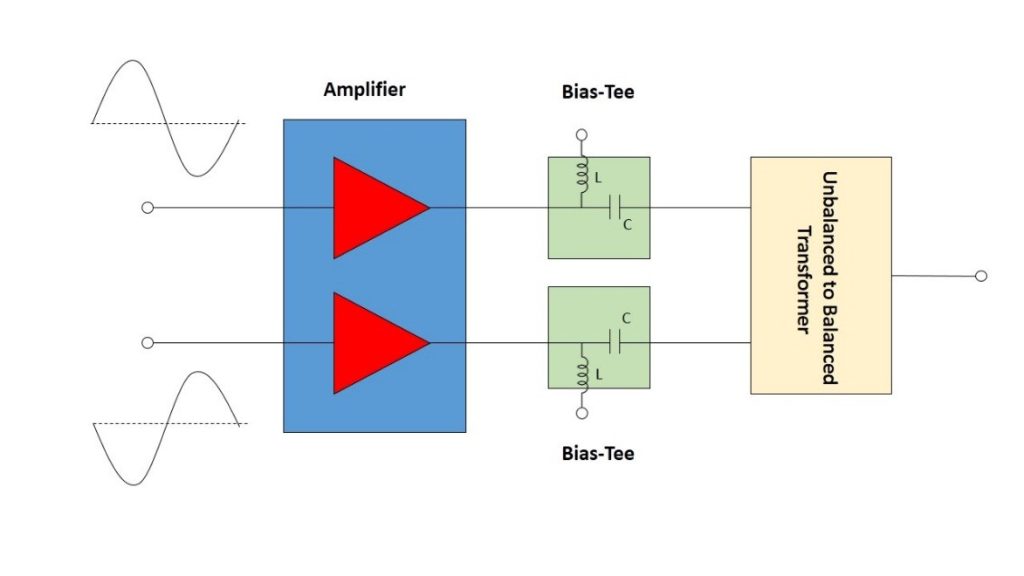
מגברי Push-Pull (דחף-סחב) משמשים במערכות מרובות אוקטבות כדי לשפר את הספק המוצא והנצילות של המגבר, לדכא הרמוניות לא רצויות ולשפר את הטווח הדינמי של המערכת. בתכנון של מגבר Push-Pull אות המקור מסופק לשני טרנזיסטורים או מגברים מתואמים במקביל וביחס מופע (פאזה) של 180º. כאשר מחברים אותם מחדש בעזרת התקן מסכם שני בהזזת מופע של 180º, האותות הבסיסיים נמצאים במופע אחד ובסיכום של פעמיים ההספק של כל מחצית, שעה שההרמוניות מסדר זוגי הן במופע הפוך, וכך מתבטלים באופן אידיאלי האותות הבלתי רצויים האלו. במציאות, חוסר האיזון של המופע והמשרעת (אמפליטודה) של מעגלי הפיצול והסיכום גורם ל”קלקול” של הביטול האידיאלי. עם זאת, התוצאה הנקייה היא עדיין דיכוי משמעותי של ההרמוניות הזוגיות, בדרך כלל ב- 20 dB עד 40 dB.
שימוש במטריצות מיתוג של Mini-Circuits ביישומי בדיקה של מערכות טלוויזיה בכבלים ל- Ω75
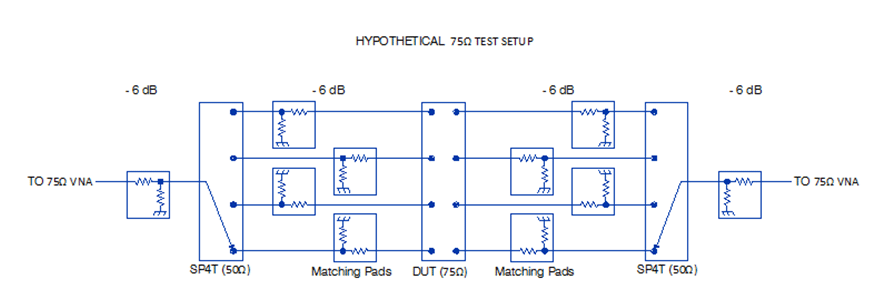
ציוד שפועל ב- Ω75 שמשמש לעתים קרובות ביישומים של טלוויזיה בכבלים (CATV), מהווה נישה קטנה בתחום הנרחב יותר שמשתמש ב- Ω50. אמנם פריטי ציוד ייעודיים ל- Ω75 קיימים, אך הזמינות שלהם ואפשרויות היישום שלהם לדרישות בדיקה אחרות הן מוגבלות; רוב פריטי ציוד הרב תכליתיים שמשמשים לבדיקה ולמדידה מתוכננים לשימוש ב- Ω50. לכן, לא קל לבנות מערכי בדיקה עם ציוד ייעודי ל- Ω75 בלבד..
Modeling Grounding and Substrate Effects in Broadband Miniature Surface Mount Attenuators
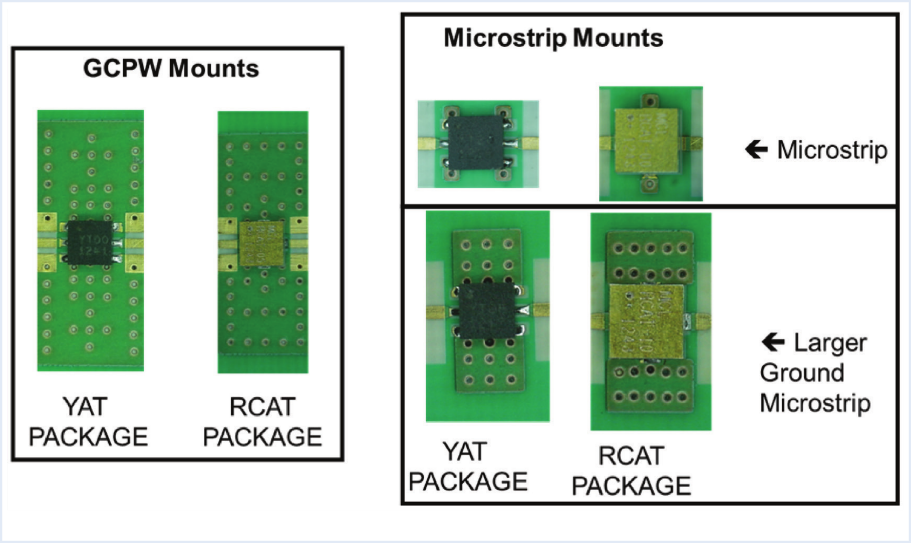
Modelithics and Mini-Circuits have collaborated to create Microwave Global Models™ for Mini-Circuits’ YAT and RCAT broadband surface mount attenuator families. These attenuators can be used to reduce signal levels, increase isolation, or improve impedance-match and retur-loss performance. Both the plastic QFN package style YAT Series and the hermetic, ceramic cavity RCAT Series are available in a tiny 2mm x 2mm footprint. The key to Mini-Circuits’ YAT and RCAT attenuators’ small size, excellent uniformity, and 2W power rating is the GaAs semiconductor fabrication process having through-wafer Cu metallization vias to realize low thermal resistance and wideband operation. Available values range from 0 to 30 dB and these components are well matched to 50 ohms over the entire DC to 18/20 GHz specification range.
Using Mini-Circuits Switch Matrices in 75Ω CATV Test Applications
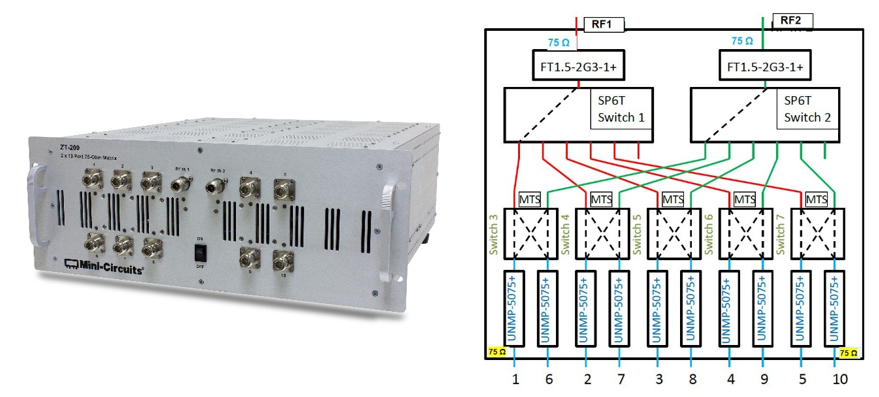
The 75Ω equipment often used in CATV applications occupies a small enclave of a largely 50Ω world. Although dedicated 75Ω equipment does exist, its availability and its applicability to other test needs are limited; most general-purpose test and measurement equipment is designed for 50Ω use. Because of this, it can be difficult to create test setups entirely out of dedicated 75Ω test equipment.
Pairing Mixers with Reflectionless Filters to Improve System Performance
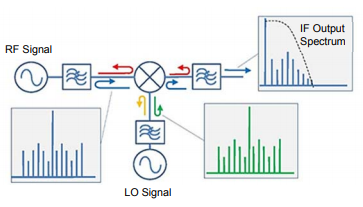
Traditional filter designs employ circuits which reject undesired signals by reflecting them back to the source. There are many applications in which these reflections produce intermodulation products, gain ripples and other problems in system performance. Non-linear devices such as mixers respond to out-of-band frequencies and are highly sensitive to the reflections caused by conventional filter designs. This becomes especially challenging as filters are often needed near or adjacent to mixers to better define bandwidth or suppress unwanted harmonics.
Eliminating Bias Tees from Push-Pull Amplifier Outputs Using TCM3-452X+ 3:1 Unbalanced-to-Balanced Transformer
Push-pull amplifiers are used in many multi-octave systems to enhance amplifier output power and efficiency, suppress unwanted harmonics and improve system dynamic range. In a push-pull amplifier design, two matched transistors or amplifiers are supplied by the source signal in parallel and at a 180° phase relationship. When re-combined through a second 180° phase shifting combiner, the fundamental signals are in-phase and combined at twice the power of each half, while the even order harmonics are out-of-phase, creating ideal cancellation of these unwanted signals. In reality, the phase and amplitude unbalance of the splitting-combining circuits result in degradation of the ideal cancellation. However, the net result is still significant suppression of the even harmonics, typically by 20 to 40 dB.
Techniques for Improving Impedance Mismatch
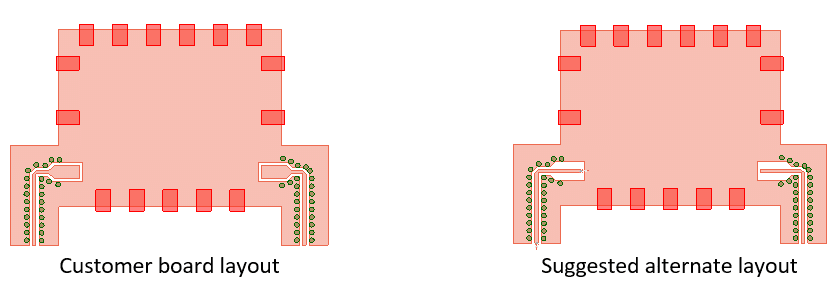
Impedance matching is a complex subject cloaked in a certain degree of mystery. Whenever a circuit fails or systemic problems are encountered, impedance matching is most often attributed as the cause. As a result, there are many situations in which it becomes necessary to match the impedance of a load to that of the source in order to maximize power transfer. There are many different techniques for impedance matching, and the best application of each will depend on the situation. This article will review the basics of impedance matching and describe some of the effective techniques commonly used to overcome impedance mismatch in a circuit.




